The axis displacement of CNC machine tools refers to the positional changes of each axis in CNC machine tools, which is of great significance for the machining accuracy, efficiency, and stability of CNC machine tools. The importance of axis displacement in CNC machine tools is as follows:
1. Machining accuracy: The accuracy of CNC machine tool axis displacement directly affects the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the machined parts. Only by ensuring the accuracy of the positions of each axis can we ensure the production of parts that meet the requirements.
2. Processing efficiency: By monitoring and controlling axis displacement, CNC systems can achieve high-speed and efficient processing, improve production efficiency, and shorten processing cycles.
3. Automation level: Accurate detection and control of CNC machine tool shaft displacement can achieve automated processing, reduce manual intervention, and improve production efficiency and stability.
4. Fault diagnosis: By monitoring the changes in axis displacement, machine tool faults or abnormal situations can be detected in a timely manner, helping with fault diagnosis and maintenance, and ensuring the normal operation of the machine tool.
5. Quality control: Accurate monitoring of shaft displacement can help achieve quality control during the machining process, ensuring that the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the machined parts meet the requirements.
In summary, the weight of CNC machine tool shaft displacement is 1. Processing accuracy: The accuracy of CNC machine tool shaft displacement directly affects the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the processed parts. Only by ensuring the accuracy of the positions of each axis can we ensure the production of parts that meet the requirements.
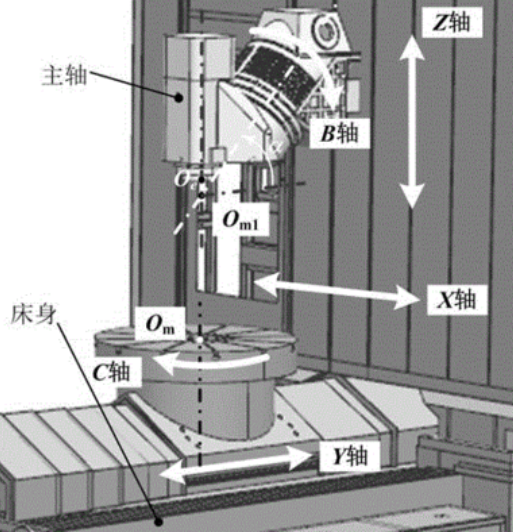
The detection of the displacement status of CNC machine tool axes refers to the detection of the displacement status of each axis of the CNC machine tool through sensors, to ensure that the machine tool can accurately control the position and motion of each axis during the machining process. Common detection methods include:
1.Encoder detection: By installing encoders on each axis of the machine tool, the position and motion status of the axis are detected in real time, and feedback is provided to the CNC system for control.
2. Displacement sensor detection: By installing displacement sensors on each axis of the machine tool, the displacement of the axis is detected to ensure accurate position of the axis.
3. Inertial sensor detection: By installing an inertial sensor on the machine tool, the acceleration and angular velocity of the machine tool are detected to determine its motion status and position.
Through the above detection methods, the displacement status of each axis of the CNC machine tool can be monitored in real time, ensuring that the machine tool can accurately control the position and motion of each axis during the machining process, improving machining accuracy and efficiency.
Senther sensor recommendation
The D8081 (including signal regulator) displacement measurement system can directly output a voltage signal proportional to the distance between the probe and the surface of the conductive object being measured. This sensing scheme can simultaneously measure both static (position) and dynamic (vibration) displacement values. This device is particularly suitable for vibration and position measurement of sliding bearing machines, as well as phase reference and speed measurement.This eddy current displacement sensor system provides state-of-the-art performance, including excellent linear range, accuracy, and temperature stability. All D8081 sensors have good parameter consistency and support interchangeability of probes, expansion cables, and proxies, without the need for special matching or calibration of various components.The D8081 displacement sensor has good long-term reliability, high sensitivity, strong anti-interference ability, non-contact measurement, fast response speed, and is not affected by media such as oil and water. It is often used for long-term real-time monitoring of parameters such as shaft displacement, shaft vibration, and shaft speed of large rotating machinery, in order to analyze the working condition and fault causes of the equipment, effectively protect the equipment and carry out predictive maintenance.


